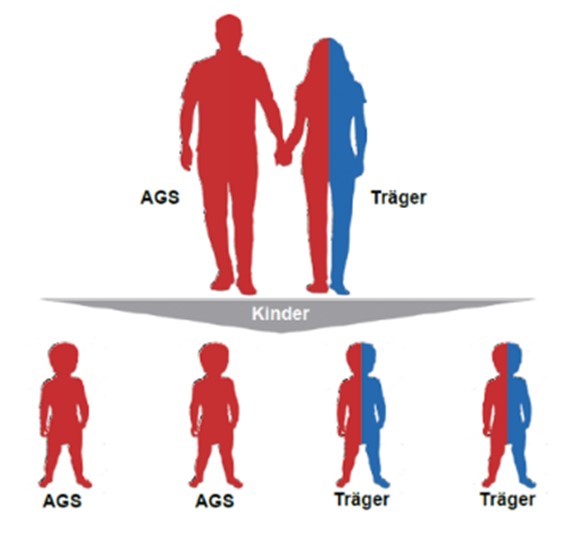
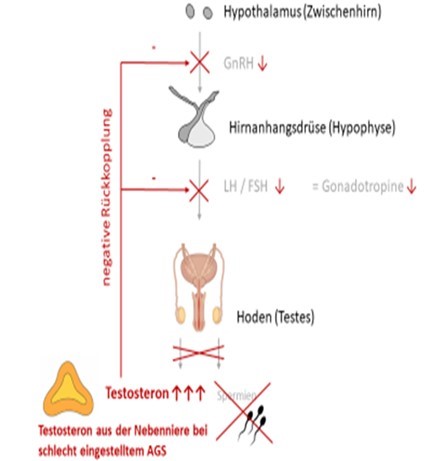
CAH in (Young) Adults
In this section, you will learn about possible changes regarding medication management starting in young adulthood, as well as all essential preventive medical checkups. The so-called “transitional medicine” ensures a successful shift from pediatric endocrinology to adult endocrinology.
After growth is complete, it is generally possible to switch from hydrocortisone to longer-acting, synthetically manufactured glucocorticoid preparations such as prednisone or dexamethasone. The advantage is that, due to their longer duration of action, prednisone only needs to be taken twice daily and dexamethasone only once daily. However, prednisone and dexamethasone are significantly stronger, meaning that side effects such as high blood pressure, weight gain, stretch marks (striae), acne, and reduced glucose tolerance (diabetic metabolic state) occur more frequently. In principle, hydrocortisone is most similar to the body’s own cortisol and therefore also the most tolerable. In the meantime, a hydrocortisone preparation with delayed release has also been developed specifically for people with AGS. This only needs to be taken twice a day – in the morning right after waking up and in the evening before going to bed.